Since its outbreak in China, COVID-19 has remained in global headlines across the world.
The virus recently made its way onto the African content and although four African countries (Tunisia, Egypt, Nigeria and Algeria) have reported cases of infected patients, the virus seems to be spreading slower in the tropics as compared to other continents.
This has led some health professionals to question if the virus is one that can thrive in the African climate or its outbreak has just been managed properly across borders. No one knows for sure how the virus will affect the African continent as well as the rest of the world.
There is however, one thing that is certain – contracting COVID-19 may not be the end of your world.
The virus has spent some amount of time touring the western part of the world and has claimed a little over 3,000 lives out of 100, 224 reported cases as at 18:00 GMT on 2nd March, 2020.
Looking at the available stats, the gap between reported cases and dead victims is significantly low. This begs the question of whether the virus is as fatal as we fear it to be.
Currently, there is no known cure for the virus. To some extent, this feeds into the terminal perception. One might believe that if there’s no way to stop it, then surely there is no way to survive it.
Among the 100,224 reported cases are 45,702 cases of patients who have made a full recovery from the virus. Does this mean the virus is not as deadly as it seems? Perhaps, yes.
According to various health experts, the elderly and the sick are among the groups of people more likely to be severely affected by the virus:
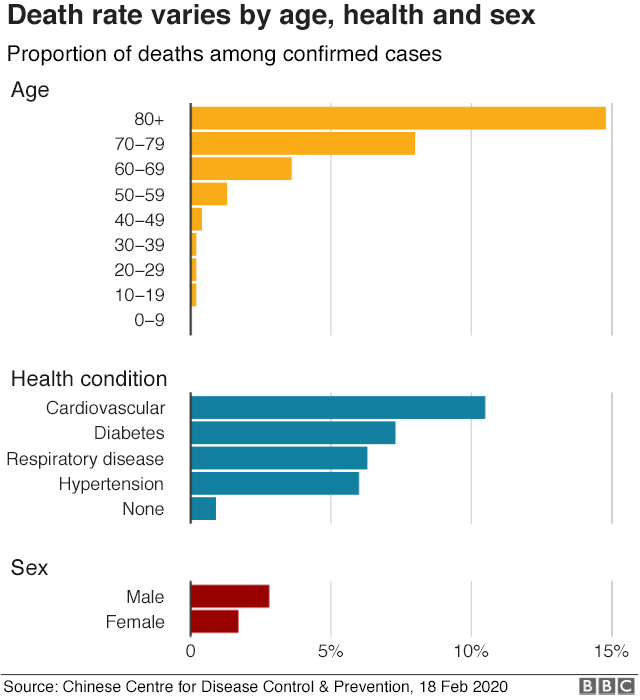
In the epicenter of the outbreak, the mortality rate is at 2%, compared to SARS (a virus which also broke out in China in 2002) which had a rate of 10%. Although the World Health Organization declared COVID-19 as a public health emergency, it has yet to be claimed as a pandemic. Though the spread of the virus outside China is an issue of concern, its low fatality rates offer some hope of curbing its development.
One of the major issues concerning the virus is its transmission as due to the flu-like nature of the virus, it spreads faster between people.
A lack of vaccine for the virus makes it harder for people with respiratory problems to protect themselves from it. Hand-washing and avoiding people who seem unwell is crucially advised.